When comparing piston valves and conventional globe valves in industrial systems, distinct differences in design and functional characteristics become apparent. Both valve types are used for flow control and shut-off applications. However, due to their specific properties, they are applied in different operating environments.
Globe valves are a design variant of seat valves and represent a standard solution in plant engineering with a long history and a wide range of applications. Piston valves are an independent valve design which – historically influenced by early developments in the 19th century – have likewise been an integral part of the process industry for a very long time. The following sections compare the key aspects of piston valves and seat valves in their function as globe valves:
Operating Principle, Torque, and Actuation Behavior
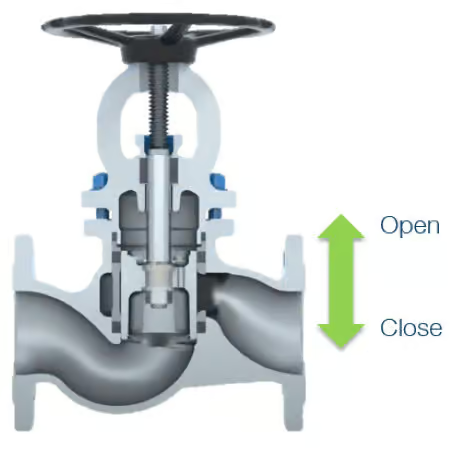
Piston Valve
Piston valves utilize a cylindrical piston guided by two sealing/valve rings, positioning the sealing surfaces outside the main flow path when the valve is open. As a result, the operating torque remains nearly constant throughout the entire stroke.
Due to the linear piston movement and the internal sealing arrangement, the torque profile remains largely uniform over the full travel range. This leads to smoother handling during manual or automated operation, as no sudden torque peaks occur when the piston contacts or disengages from a seat.
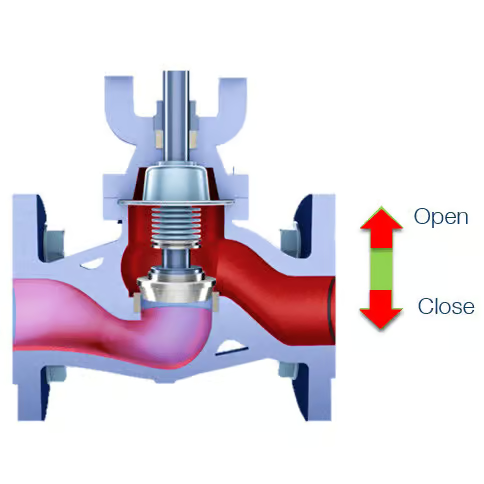
Globe Valve
In conventional globe valves, the required operating torque increases significantly as the closure element approaches the seat or is lifted from it. This characteristic torque peak is inherent to the design and results from the direct contact between the plug and the seat.
Impact on Seat and Sealing System
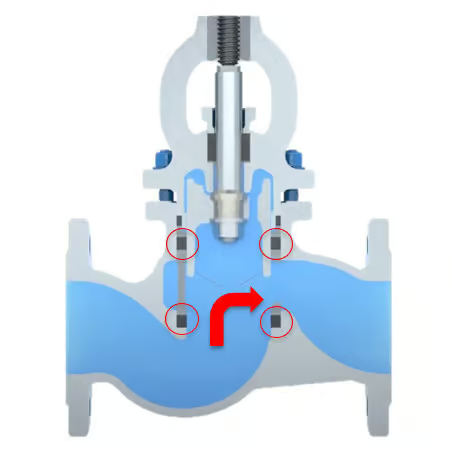
Piston Valve
In the open position, the sealing surfaces of many piston valves are not directly exposed to the main flow field, which minimizes erosion of the sealing elements and seat.
The KLINGER piston valve is the first valve design to feature an elastic, replaceable sealing system suitable for higher temperature ranges.
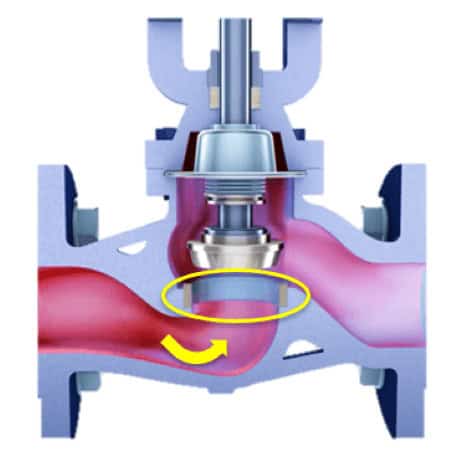
Globe Valve
In globe valves, the seat system is located directly in the flow path and could be therefore continuously exposed to the process medium. In addition, temperature fluctuations and pressure differentials can increase the load on the sealing surfaces, as thermal and mechanical forces act directly on the seat system.
Particles in the Process Medium
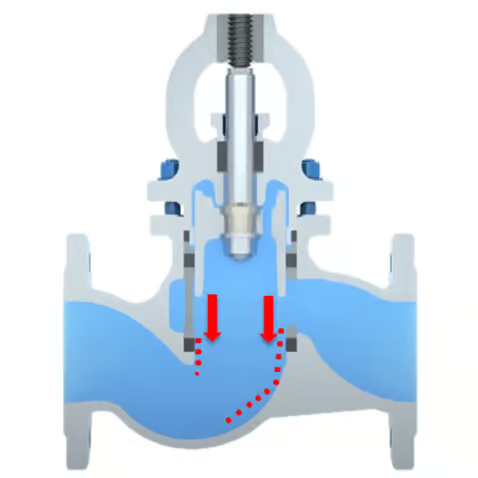
Piston Valve
The piston movement can displace particles out of the sealing area instead of allowing the to become permanently embedded – a “self-cleaning effect” that is particularly advantageous in contaminated media. This significantly reduces leakage risks caused by trapped particles.
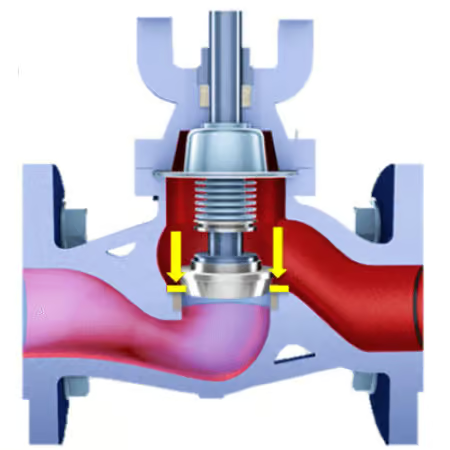
Globe Valve
Particles in the medium tend to accumulate on the seat surfaces and will be pressed into the seat by the piston and sealing area by closing forces, which can lead to increased wear over time.
Maintenance and Service
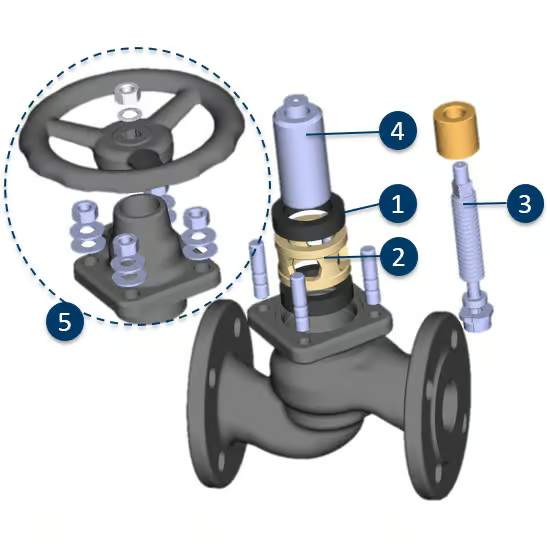
Piston Valve
Many piston valves are designed so that maintenance work and replacement of wear parts can be performed without removing the valve from the piping system (“inline”). This reduces downtime and simplifies maintenance procedures. However, servicing should only be carried out when the valve is in a depressurized state.
Globe Valve
With conventional globe valves, access to the seat and sealing components often requires removal from the pipeline or extensive disassembly, which can significantly increase maintenance effort, particularly for larger nominal sizes.
Historical Background

Piston Valve
Piston valves have a long tradition as steam valves. They were first mentioned in the 19th century and use a cylindrical piston guided by sealing systems instead of a disc and a seat.
A major milestone was Richard Klinger’s development of a valve in 1922 (KVN), in which he replaced the conventional seat valve sealing system with a cylindrical piston featuring two elastic, replaceable seals. This innovative solution has provided high tightness and simplified maintenance under temperature and pressure fluctuations for more than 100 years.
Modern piston valves therefore combine a more streamlined flow path with protection of the sealing elements from direct erosion, while also enabling comparatively simple seal replacement during service. This makes them a durable and operationally reliable alternative to conventional globe valves, particularly in steam and condensate systems.

Globe Valve
In the 19th century, globe valves evolved from early steam and water valves and become one of the defining valve types of industrialization.
Their operating principle is based on a disc that is pressed onto a seat via stem, thereby defining the flow cross-section. This design is well suited for precise control tasks but features a comparatively tortuous flow path, which can promote pressure loss and erosion.
Over the decades, numerous variants and patents have emerged; however, all are fundamentally based on this classic seat valve principle, which has become established as a robust but more maintenance-intensive standard-design, particularly in steam and process piping.
KLINGER Product Portfolio
Plant engineers, designers, and operators can find both piston valves and conventional globe/seat valves within the KLINGER Group’s product portfolio. Through a global sales and service network, both valve types are available, ensuring suitable solutions for a wide range of process requirements.



